之前一直在做分类网路的工作,物体检测网络有了解,但是还没有从头训练过,这次通过几天时间的集中学习,终于理解了整个网络的大部分细节,这里作简要记录。
思维导图
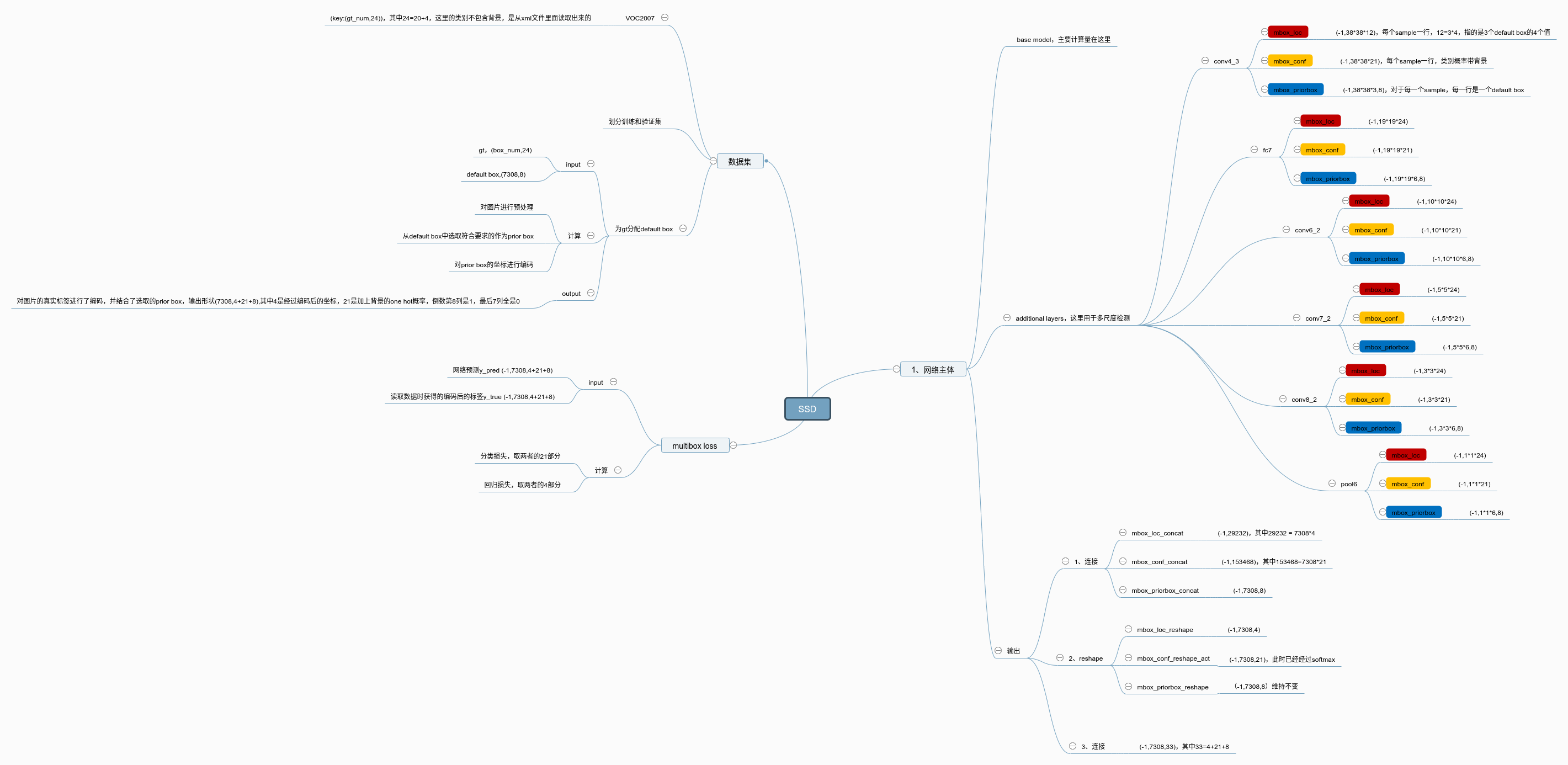
简要总结
- 网络部分: 最终输出的是一个封装好的数据,封装的什么呢?三部分,1、每个default box的分类损失,2、每个default box的回归损失,3、生成的default box的坐标,长度为8,四个坐标加上四个varance值辅助训练。
- 数据部分:我么先读取训练数据,可以获得gt box的两个坐标以及所属类别,然后我们也知道,并不是多有的default box都参与训练,而是符合一定要求的才参与训练(IOU大于阈值,并且一个default box只对应一个gt box),经过筛选后,每个gt box会和一个或几个default box对应,此时我们称这些default box为prior box,这也是很多博客里面说的,default box是客观存在的,不管你输入是是什么,而prior box是实际采用的,因为随着图片的不同,gt box的位置不同,prior box也不同。最后再对原始的绝对坐标进行编码。
- 损失部分:损失是计算上述两者的输出,均是(-1,num_default_box,4+21+8)(在VOC2007下,base model为VGG16),在损失这部分还有一个值得注意的地方就是hard mining,通过控制正负样本的比例来辅助训练。
-
代码
随后我会将代码(参考:Github)上传到我的github上,对比参考的代码,我只是在里面添加了中文注释,并根据最新版本的keras进行了API修改。
xml_processor.py
1 | |
最后将读取到的数据(主要是文件名、类别和box坐标)设计成字典:{file_name: [num_box,4+20]},其中4是四个坐标为物体的坐标,20为one_hot类型的类别标签。这是个通用的处理函数,一般voc格式的xml文件都可以使用。
ssd_train.py
1 | |
这里面主要是y = self.bbox_util.assign_boxes(y)这句代码,作用是为gt box(ground truth box)配default box,为什么要分配呢?我们知道,default box的数量是根据feature maps的尺寸决定的,也就是不管你来的是哪张训练图片,图片中有几个gt box,default box就在那里,不增不减,但是我们并不会将所有的default box参与训练,我们只训练那些接近gt box的default box,这也是为了让网络能够顺利训练设计的,选取出来的default box又被成为prior box。
bbox_utils.py
1 | |